producer's equilibrium
meaning of producer.
producer is a person who produces goods and services for sale and his objective is profit maximization.
Q2 define producer's equilibrium
Ans. the word equilibrium in economics has been taken from physics where it means, state of rest. but in economics it is used in different sense. so, producer's equilibrium is a situation where producer is in best possible situation. for eg. : if a producer gets maximum profits than he will in equilibrium where as in the situation of losses he gets minimum losses then producer is said to be in equilibrium and here he has no tendency to move away from the equilibrium situation.
Q3. what are various approaches to determine producer's equilibrium.
Ans. there are two approaches to determine producer's equilibrium:
i) TR and TC approach
ii) MR and MC approach
Q4 explain the producer's equilibrium with the help of MR and MC approach?
or
what is the general profit maximization condition of a firm?
or
show that a perfectly competitive firm maximizes its profit only when price = MC?
i) when MR is in straight line or P.E. under perfect competition :-
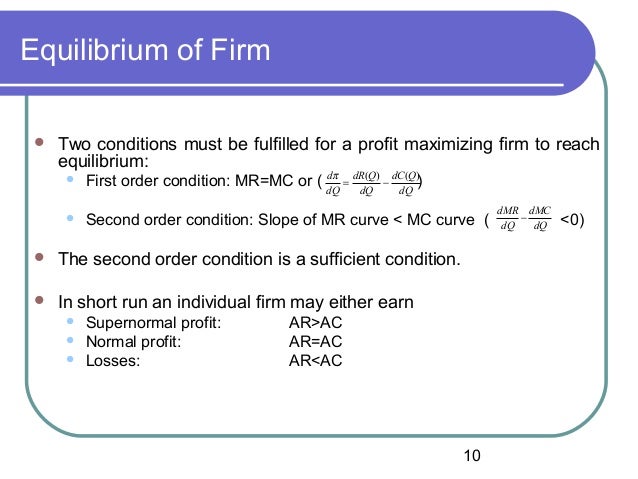
A producer is said to be in equilibrium when given level of output gives him maximum profit and he has no intention to change the level of output . with a view to maximise his profits, a produce upto that quantity at which following two conditions are fulfilled.
MC = MR MC cuts MR from below.
output MR MC
1 10 8
2 10 7
3 10 6
4 10 8
5 10 10
6 10 13
the table is drawn on the assumption that price (AR) is constant so MR is constant (10) we are assuming a situation of perfect competition. the table shows that two conditions are satisfied only when 5 units are produce :-
i) MR = MC
ii) MC, is cutting MR from Below. (MC is rising )
the producer's equilibrium can be explained with the help of table and diagram.
we consider equilibrium of a producer who is working under conditions of perfect competition and takes the price of the product as given and constant for him.

condition - I MC = MR
if the producer produces OM units, he can increase profits of the firm = T as MR = MC MC cuts MR from its below thus he want to increase production to OS, so as it earn maximum profits.
if on the other hand, the producer produces 400 units, then he suffers losses = after point T as MC >MR, so the producer will prefer to produce till 350 units, where MC = MR, MR is rising and profit maximum.
condition-2 MC is rising
in the diagram MC curve cuts MR curve at point K and T. at point K , firm produces OM units of output, as the firm increase its output from OR units of output, as the firm increases its output from OR to OQ initially its MC will go to falling but MC is less than MR it means productions from OR to OQ will add to the profits of the firm.
this point K cannot be the point of equilibrium of the firms thus point E represent producer's equilibrium as at this point MC = MR and MC is rising.
Q5 explain producer's equilibrium with MC and MR method under imperfect competition?
Ans- ii) when MR curve is downward sloping
according to this approach a producer will be in equilibrium when following two conditions are satisfied.
i) MC = MR
ii) MC cuts MR from below
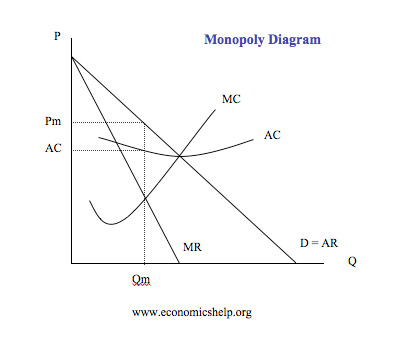
i) MC = MR
MC = MR and MC is cutting MR from below, so here a producer will be in equilibrium.
ii) MR > MC
MR > MC, so here a firm will get profits. therefore a producer will increase output.
Q6 explain the determination of short run equilibrium of the firm under perfect competition?
Ans- producer's equilibrium - short period and long period analysis
short period :-
it is a time period in which new firms cannot join the industry and existing firm cannot leave the industry.
in short period a firm or producer will be in equilibrium when following two conditions are satisfied
i) MC = MR
ii) MC, uts MR from below
in short period firm may have to face following three situations.
1. super normal profits or abnormal profits or extra normal profits :-
a firm will get super normal profits when price becomes greater than AC . or when TR >TC.


2. normal profits or zero abnormal profits:-
a firm will get normal profits when price becomes equal to AC. TR = TC.

3.abnormal losses or extra normal losses:-
a firm will get losses when AC becomes greater than price. TR <TC.
AR < AC

Q8- what is shut down point ?
Ans- shut down point
it is the point where price becomes equal to AVC

price = AVC , so it is called shut down point.
gross profits = TR - TVC
net profits = TR - TC
Q9- only a rising segment of MC curve starting from the shut down point is considered as a short period supply curve of a firm. explain/
Ans- a competitive firm strikes its equilibrium, when at a given price, MR = MC and MC is rising. during the short period a firm will undertake production only if AR or P > AVC i.e. a short period supply curve of the firm starts from its shut down point, where P = AVC starting run supply curve would be the same as its MC curve which shows the price + quantity relationship.

In the diagram, the firm is in equilibrium where MR = MC and MC is rising.
P = AVC ( shut down point ) which is the starting point of firm's supply curve producing OQ quantity. when price increases the firm strikes equilibrium , and the firm produces OQ1 quantity. thus during the short period, rising segment of MC curve ( starting from the shut down point ) is the same as the firm's supply curve as it shows positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Q11. the break even point and shut down points are different how?
Ans. break even point occurs when the firm's total revenue is equal to the total cost i.e. no profit no lose situation.
TR = TC or AR = AC
shut down point is the point at which the market price of the product is equal to the AVC. fixed costs are not recovered at this point. the firm continuous production till this point as at least the variable costs is being recovered.
TR = TVC or AR = AVC
\







No comments:
Post a Comment